Western Blot
The western blot technique is an expedient method for the identification of specific proteins from a complex mixture. After extraction of the protein mixture, e.g. via cell lysis, the first step is to separate the proteins based on their molecular weight using gel electrophoresis. For protein separation by size, usually a polyacrylamide gel is prepared. Next, the proteins are transferred or blotted from the gel to a solid support, generally a nitrocellulose or polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) membrane. Because of its efficiency and speed, electrophoretic transfer is the most common blotting procedure. The gel and the membrane are “sandwiched” between two electrodes and the proteins are transferred due to their electrophoretic mobility, influenced by factors such as charge and size.
Since the membranes have a high affinity for proteins, the remaining binding sites of the surface need to be blocked after the transfer to prevent unspecific binding of the detection antibodies. A variety of different buffers and reagents is used in the whole process and, to minimize the signal-to-noise ratio, sufficient washing is required as intermediate step.
For detection of the antigen, it can be chosen between direct or indirect detection. For direct detection of Strep-tagged proteins, only a single labeled and target-specific antibody, such as our StrepMAB-Classic conjugated to HRP, is required. While it is quite common to use antibodies for detection, our Strep-Tactin® products conjugated to HRP or AP represent an equally beneficial alternative. These products are based on our Strep-tag® technology.
The combination of a primary antibody detecting the target and a labeled secondary antibody is widely used as well, as the second antibody leads to a signal amplification and provides different options for multiple detection methods. The choice of primary and secondary antibody depends on various parameters, such as the origin of the target protein, the species of the primary antibody or the desired detection method. When working with Strep-tagged proteins, our murine StrepMAB-Classic antibody is a good choice as primary antibody.
Nowadays widely applied labels are fluorophores or enzymes. As in the case of ELISA, horse-radish peroxidase (HRP) or alkaline phosphatase (AP) are the most common enzymes. Even though enzymatic labels require extra steps and usually have to be optimized, they are used most extensively due to the high sensitivity and the flexibility in detection when choosing between chromogenic, fluorogenic, and chemiluminescent substrates. When using fluorophores as labels, fewer steps are required, since no substrate development is necessary. For this purpose, we offer various fluorescent labels conjugated to Strep-Tactin®XT, StrepMAB-Immo or StrepMAB-Classic. The choice of the experimental procedure is generally dependent on the laboratory equipment, e.g., special devices for the detection of a fluorescent signal are needed.
Altogether, the relatively easy protocol for western blots offers a broad range of potential utilizations, such as detecting post-translational-modifications or verifying protein cloning, and makes it such a popular application.
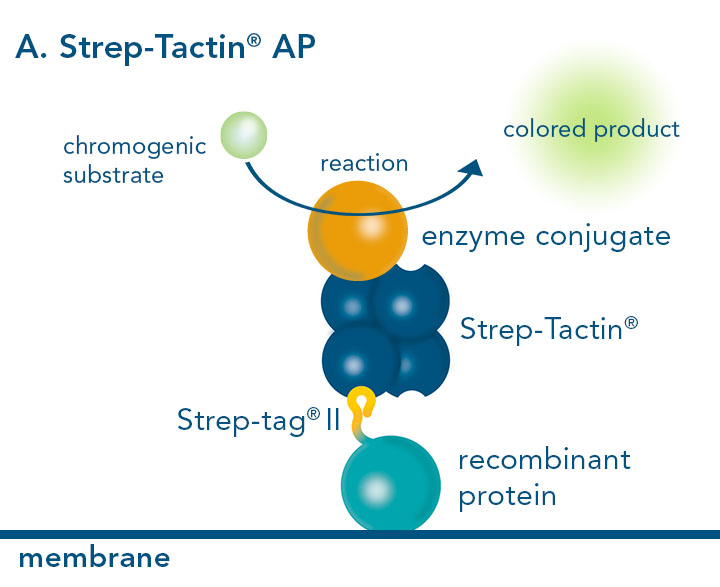
Western blot using Strep-Tactin® conjugated AP
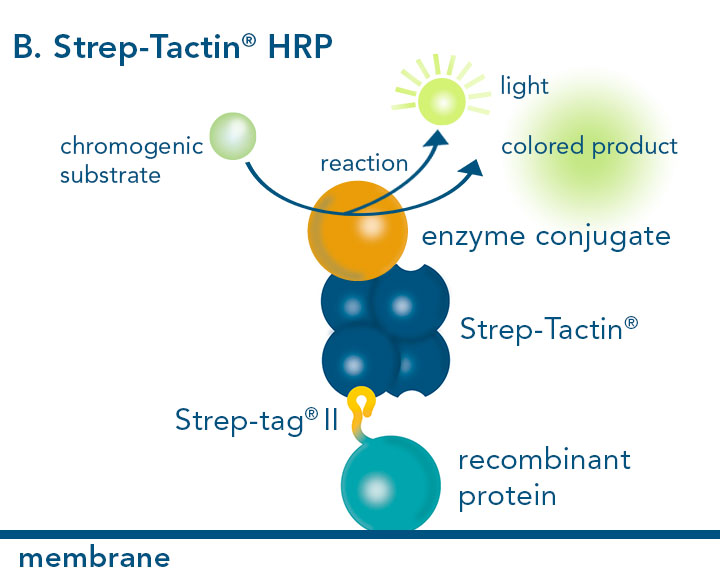
Western blot using Strep-Tactin® conjugated HRP
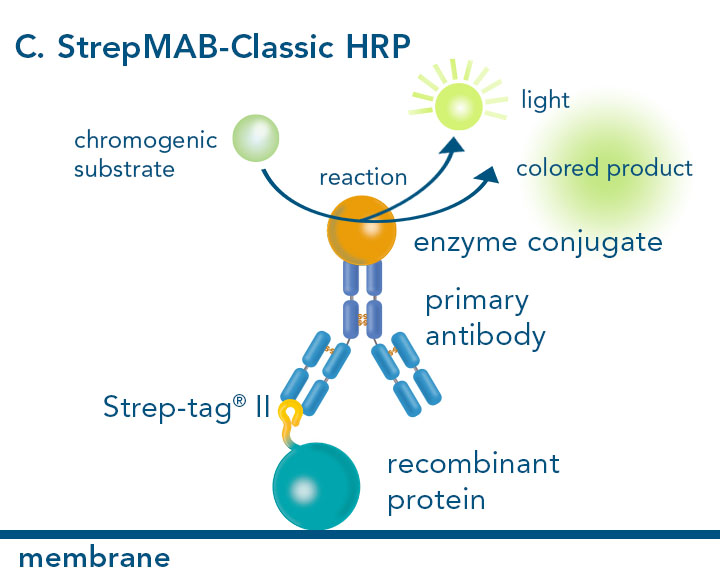
Western blot using StrepMAB-Classic conjugated HRP
Application examples
Protein detection with Strep-Tactin® Conjugates
Strep-Tactin® conjugates can be used for several assay applications. As example, the application of Strep-Tactin®HRP and Strep-Tactin®AP for Western Blot as well as Dot Blot is shown.
Strep-Tactin®HRP
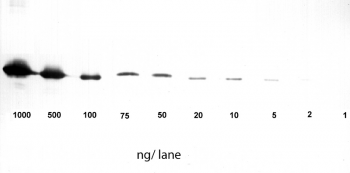
Application: Western Blot
1-1000 ng/lane of GFP C-terminally tagged with Strep-tag®II (28 kDa) were separated by SDS-PAGE and blotted onto a membrane. Detection occurred with Strep-Tactin® HRP.
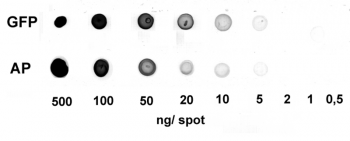
Application: Dot Blot
0.5-500 ng/spot of GFP-Strep-tagII (28 kDa) or alkaline phosphatase C-terminally tagged with Strep-tag®II (monomer 48.5 kDa) were spotted onto a membrane. Detection occurred with Strep-Tactin® HRP.
Strep-Tactin®AP
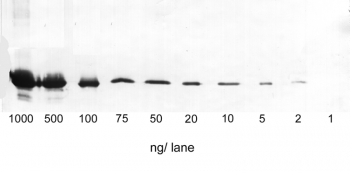
Application: Western Blot
1-1000 ng/lane of GFP C-terminally tagged with Strep-tag®II (28 kDa) were separated by SDS-PAGE and blotted onto a membrane. Detection occurred with Strep-Tactin® AP.
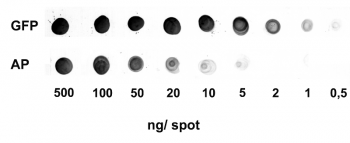
Application: Dot Blot
0.5-500 ng/spot of GFP-Strep-tagII (28 kDa) or alkaline phosphatase C-terminally tagged with Strep-tag®II (monomer 48.5 kDa) were spotted onto a membrane. Detection occurred with Strep-Tactin® AP.

